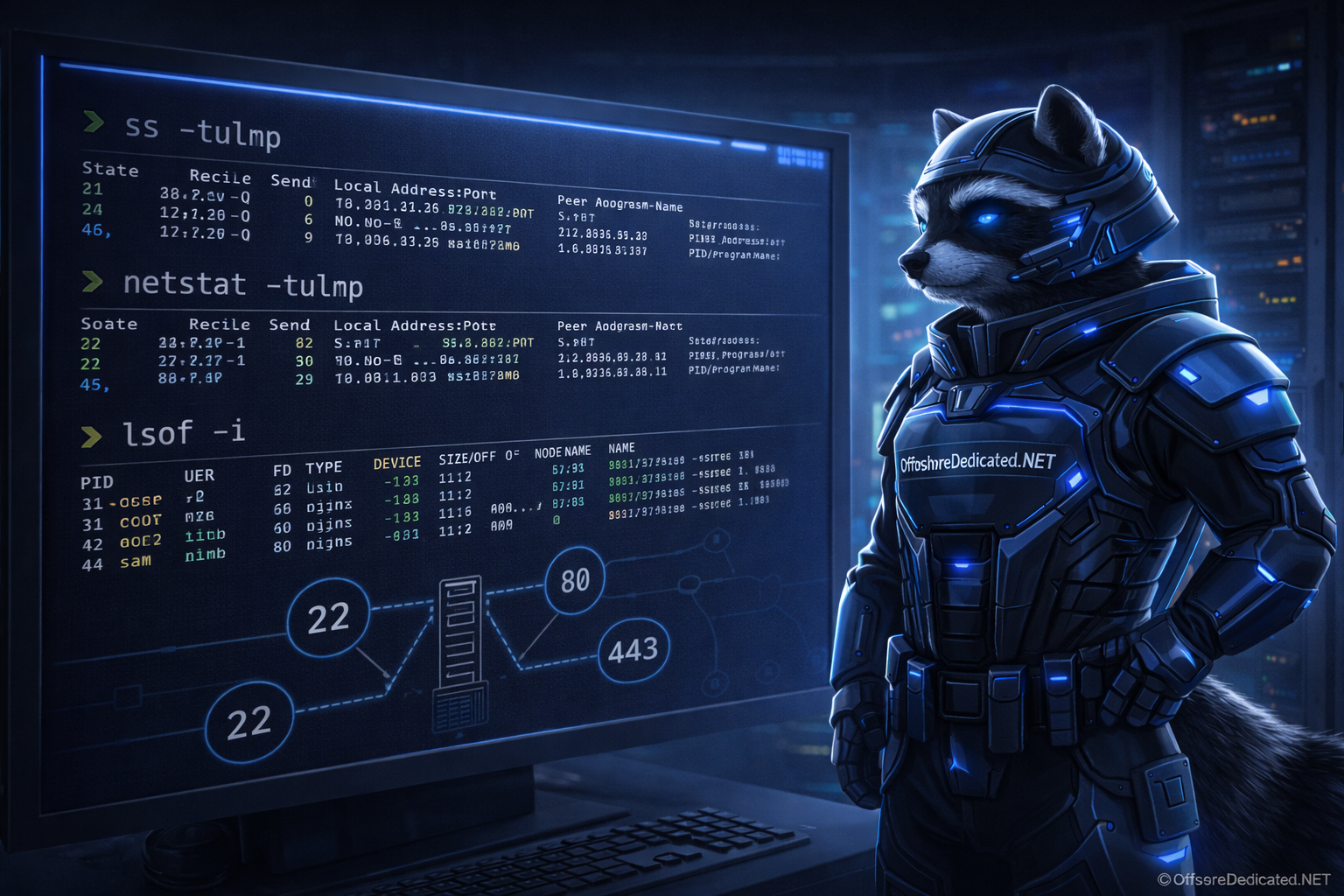
How to Check Open Ports in Linux (ss, netstat, lsof Explained)
Open ports determine how services communicate with the outside world. Web servers, databases, control panels, streaming services, and SSH access all rely on specific network ports being open and listening.